list_for_each(), list_for_each_entry() 함수에 대해서 알아보도록 하곘습니다.
리눅스 커널에서 자주 사용되는 함수로, 링크드 리스트를 이용하는 함수들 입니다.
<linux/list.h>에는 여러 함수가 있지만, 중요한 함수 부터 알아보도록 하곘습니다.
링크드 리스트
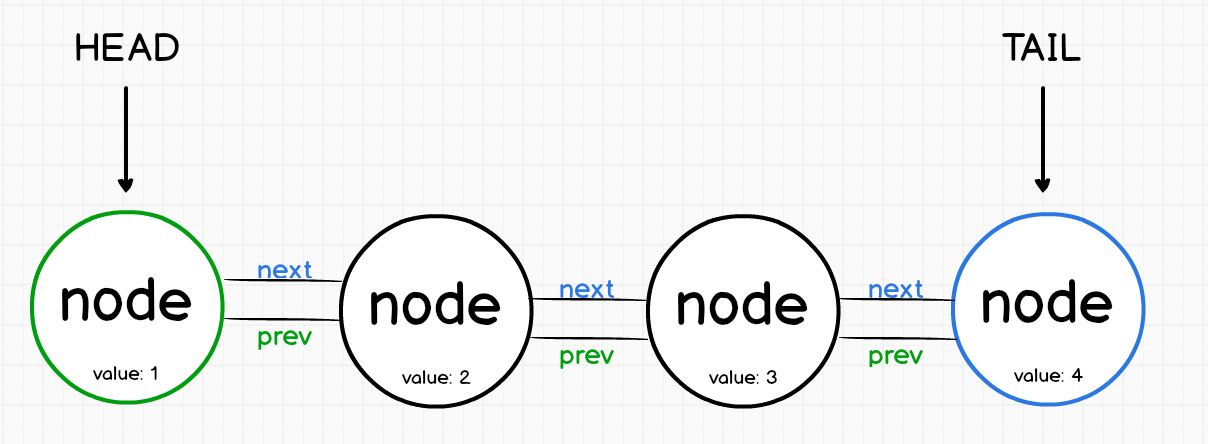
1. list_for_each() 함수
list_for_each() 함수는 리스트를 순회합니다.
1.1 Include
list_for_each() 함수는 <linux/list.h>에 선언되어있습니다.
#include <linux/list.h >
1.2 Function
함수의 원형은 다음과 같습니다.
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
1.3 Parameters
list_for_each() 함수는 3개의 파라미터를 갖습니다.
- pos
- 루프문에서 사용할 커서로써 항목을 임시로 저장해두는 변수이다.
- head
- 리스트의 헤드(가장 앞)로 연결 리스트의 시작 주소 입니다.
1.4 Example
struct list_head *ptr;
struct list_node *node;
list_for_each(ptr, &my_list){
node = list_entry(ptr, struct list_node, list);
}
2. list_for_each_entry() 함수
list_for_each_entry()는 for 문 처럼 각각의 node는 순서대로 접근 하는 함수 입니다.
2.1 Include
list_for_each() 함수는 <linux/list.h>에 선언되어있습니다.
#include <linux/list.h >
2.2 Function
함수의 원형은 다음과 같습니다.
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
2.3 Parameters
list_for_each_entry() 함수는 3개의 파라미터를 갖습니다.
- pos
- 루프문에서 사용할 커서로써 항목을 임시로 저장해두는 변수입니다.
- head
- 리스트의 헤드(가장 앞)로 연결 리스트의 시작 주소 입니다.
- member
- 인자는 node의 링크드 리스트의 멤버 변수 입니다.
2.4 Example
#include <linux/list.h>
struct Node{
int Data;
struct list_head list;
}
...
list_for_each_entry(curr, &my_list, list){
printf("%d\n", curr->number);
}
...